Power BI’s Incremental Refresh is a great feature that helps improve performance and efficiency when working with large datasets. Instead of loading all data every time, Power BI only refreshes new or changed records. This is especially useful when working with CSV files.
Why Use Incremental Refresh?
When dealing with large CSV files, refreshing the entire dataset every time can be slow and resource-intensive. Incremental refresh helps by:
- Reducing the data load time
- Improving performance
- Minimizing memory usage
- Refreshing only the latest data while keeping historical data intact
Steps to Set Up Incremental Refresh in Power BI for CSV
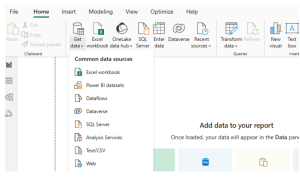
Step 1: Load CSV File into Power BI
- Open Power BI Desktop.
- Click on Home > Get Data > Text/CSV.
- Browse and select your CSV file. Click Load to import the data.
Step 2: Convert the Date Column to Date/Time Format
Incremental refresh requires a date or datetime column to filter data.
- Go to Power Query Editor (Click Transform Data).
- Select your date column and change the data type to Date/Time.
- Click Close & Apply.
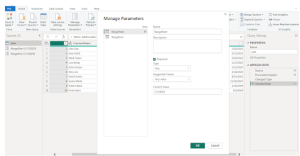
Step 3: Enable Incremental Refresh
- In the Fields pane, right-click the table and select Incremental Refresh.
- Enable Incremental Refresh & Real-Time Data.
- Set Range Start and Range End parameters:
- Define a fixed period for keeping historical data (e.g., last 2 years).
- Define a refresh period (e.g., last 7 days).
- Click Apply.
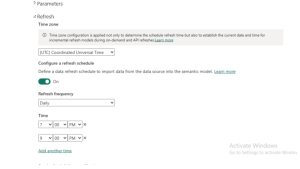
Step 4: Save and Publish the Report
- Save the Power BI file.
- Publish it to Power BI Service.
- In Power BI Service, configure a scheduled refresh under Settings > Datasets.
Important Considerations
- CSV files must be stored in a reliable location like SharePoint, OneDrive, or Azure Blob Storage.
- Ensure the date column is consistently formatted to avoid refresh errors.
- Scheduled refresh must be set up in Power BI Service for automation.
Conclusion
Using Incremental Refresh with CSV files in Power BI optimizes performance and reduces data load time. This powerful feature is especially useful when working with frequently updated datasets. Following the steps above, you can efficiently refresh only the necessary data while maintaining historical records.




