Within a project, features get modified since during the time period of a project client’s requirements might change. This could lead to some miscommunication:
For example, a client is asking for one thing and we are providing him with something else, in this case, continuous feedback is required so, for this reason, a different approach comes to light which is Agile. In Agile, we are responsible to give the client a ready product every 2 to 3 weeks, not the entire product but the parts of it. For instance, there are 10 features in a project; we can give 1 feature in 2 to 3 weeks. It will be good from the client side as we will be getting continuous feedback.
Another thing is supposed we are working on a project having certain modules and there are multiple developers working on it. So, the approach to follow is can give one module to each developer. For each developer ‘Unit testing’ will work perfectly but things could be different in the case of ‘Integration Testing’, after integration it would be then deployed to the server. Before that comes the concept of Automation Testing. But what if there are issues found after the test. To solve this issue we have a concept of Continuous integration.
Continuous Integration:
Let’s say within a day we do 6-7 commits and every time we make a change just submit it in the repository and it is tested further.
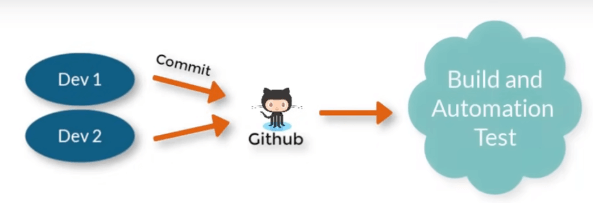
The advantage would be after each and every submission there will be an automation test i.e. write: Commit: test
So at the end or after every commit, we will be having a ready project which is tested and we have the confidence that it is working. Hence just after the moment code is ready and working fine during unit testing it should be committed so that there will be an automation test done on the server.
After this comes the concept of continuous delivery and continuous deployment:
Continuous Delivery: (Making the code available for the environment)
In case the client wants to see the progress or in case the commit we have made seems ready to us, we can simply show the client the working model on a mock server.
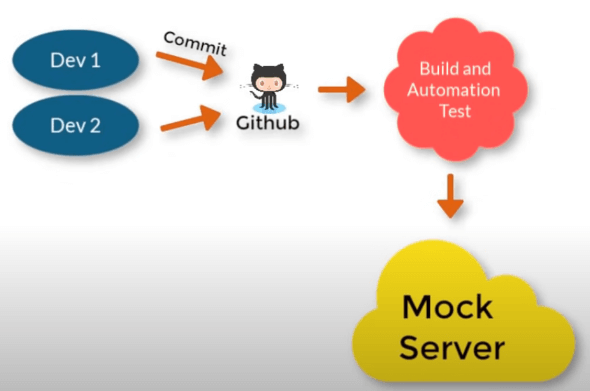
Through this we can check the performance as well as the progress of the project and the client would also be satisfied with the demo of the project module. Also, we can mimic how the project would respond after deploying that to the production environment.
Continuous Deployment:
After the commit code is tested and afterward directly deployed on the server.
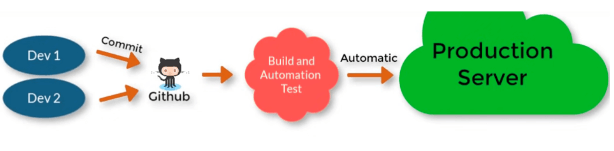
Every company has a different approach some only go for CI and some go for the other option. It is a little difficult since the team should be ready for the later issues, there should be a pipeline so that each process is done in a sequence. There are tools available for this like Jenkins that proves best for CICD.
jQuery presents a tree-like structure of all the elements on a webpage simplifying the syntax and further manipulating such elements. The jQuery Certification exam by StudySection will secure your fundamental knowledge and a basic understanding of jQuery as an asset to improve your skills.




