Bitcoin is a decentralized digital cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized peer to peer network and no single person or single administrator controls it. It was invented in 2009 by an unknown person known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It is created and held electronically. Bitcoin is a virtual currency. It can’t be printed like a dollar or euros.
Creator of Bitcoin
A software programmer by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto presented bitcoin in 2008, as an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof. The idea was to produce a means of exchange, independent of central authority, transferable in a secure and verifiable way. Nobody knows who Satoshi Nakamoto really is.
Characteristics of Bitcoin
-
- Decentralization
It’s most important characteristic is that this is decentralized, no single institution or authority controls it. It is maintained by a group of programmers and run by an open network of dedicated computers spread around the world.
- Decentralization
Bitcoin solves the double-spending problem of electronic currency by the combination of cryptography and economic incentives. The integrity of the transactions is maintained by a distributed and open network, owned by no-one.
- Limited supply
Fiat currencies can have an unlimited supply, central banks can issue as many currencies as they want and manipulate the value of the currency. Bitcoin supply is strictly controlled and defined by underlying algorithms. A low range of new bitcoins trickle out every hour and will continue to do so at a decrease rate until a maximum of 21 million has been reached. This makes it an even more valuable thing. Its value is controlled by demand and provides the currency. - Pseudonymity
Senders of traditional electronic payments are usually identified because they have to reveal their identity before using the services of any bank. In the case of bitcoin, users operate in semi-anonymity. Because there is no central authority so users do not need to identify themselves when making transactions. Each bitcoin user is identified by the address of his or her wallet. Transactions can be tracked this way. So, Law enforcement has created methods to identify users. - Immutability
Bitcoin transactions cannot be reversed unlike other fiat currencies issued by banks. If a transaction is recorded in the network, approved, and published on the public ledger, it is not possible to modify it. It means that transactions on the bitcoin network cannot tamper. This makes it secure and tamper-proof. - Divisibility
The smallest unit of a bitcoin is understood as Satoshi. It is one hundred millionth of a bitcoin i.e(0.00000001). This feature enables microtransactions that traditional economic money can not provide.
How it works
Bitcoin is a digital asset or currency. Users can create a bitcoin wallet to generate addresses of wallets and share the address with others to receive bitcoin from people. The wallet can store received bitcoins and send to other addresses when you want to.
- Balances on blockchain
Blockchain is a shared public ledger on which the complete bitcoin network relies. All confirmed transactions are published on the blockchain. It allows the associated wallets to calculate the balance of a wallet and keep track of spent and received amounts. The integrity of blockchain is ensured by cryptography. - Transactions
A transaction is an act of sending or receiving value in the wallet. Each bitcoin transaction gets recorded in the blockchain ledger. Bitcoin wallets generate a secret key with the use of cryptography. It is called a private key. A private key is used to authorize any transaction from the wallet. Once a transaction is created, it is broadcasted on the network. - Mining
Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to validate newly created transactions and confirm those. To be confirmed, transactions must be bundled in a block of fixed size that has very strict cryptographic rules. These transactions are validated by different computers that are part of the network, called minors by solving a cryptographic puzzle. Minors work in bitcoin networks to gain a reward in return for their efforts.
Example:
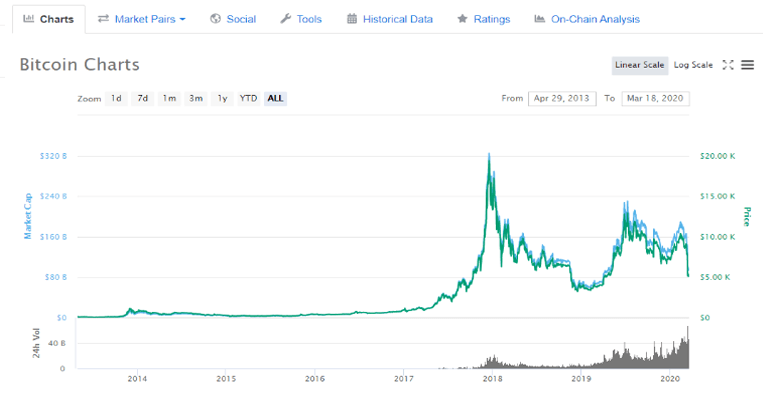
What is Bitcoin?
It is a decentralized digital cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized peer to peer network and no single person or single administrator controls it.
Who created Bitcoins?
A software programmer by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto presented bitcoin in 2008, as an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof. The idea was to produce a means of exchange, independent of central authority, transferable in a secure and verifiable way.
What is Pseudonymity?
Senders of traditional electronic payments are usually identified because they have to reveal their identity before using the services of any bank. In the case of bitcoins, users operate in semi-anonymity. Because there is no central authority so users do not need to identify themselves when making transactions.
How is Bitcoin currency secure?
Bitcoin transactions cannot be reversed unlike other fiat currencies issued by banks. If a transaction is recorded in the network, approved, and published on the public ledger, it is not possible to modify it. It means that transactions on the bitcoin network cannot tamper. This makes it secure and tamper-proof.
Get certification for your knowledge in the fundamentals of Computer functioning by clearing the Computer Certification exam conducted by StudySection. After going through this Computer Certification exam, you will be able to evaluate your basic knowledge of computers.




